From the comprehensive approach of ISO 22301 in Business Continuity Management to the specialized third-party risk management guidelines set by regulatory bodies across the United States, EMEA, and APAC regions, the universal emphasis on regular testing, senior management involvement, and stakeholder collaboration are gamechangers for organizations building the capability to withstand compound disruption.
The practice of engaging third parties and business stakeholders in building response capability are not only regulatory checkboxes but foundational capabilities that ensure adaptability to the unexpected, safeguarding critical operations and services against the backdrop of an ever-evolving risk landscape.
Global Standards for Third-Party Risk
Exercising and firm engagement are critical components of third party risk management and operational resilience, ensuring that organizations not only design effective resilience strategies but also validate and improve these strategies through regular testing and stakeholder engagement. But how do these regulations frame the requirements for engagement and how much emphasis do they put on exercising response and engaging stakeholders in the process?
To better understand this question, we’ve gone through the exercise of evaluating testing and firm engagement requirements related to third-party risk management across various standards and regulations.
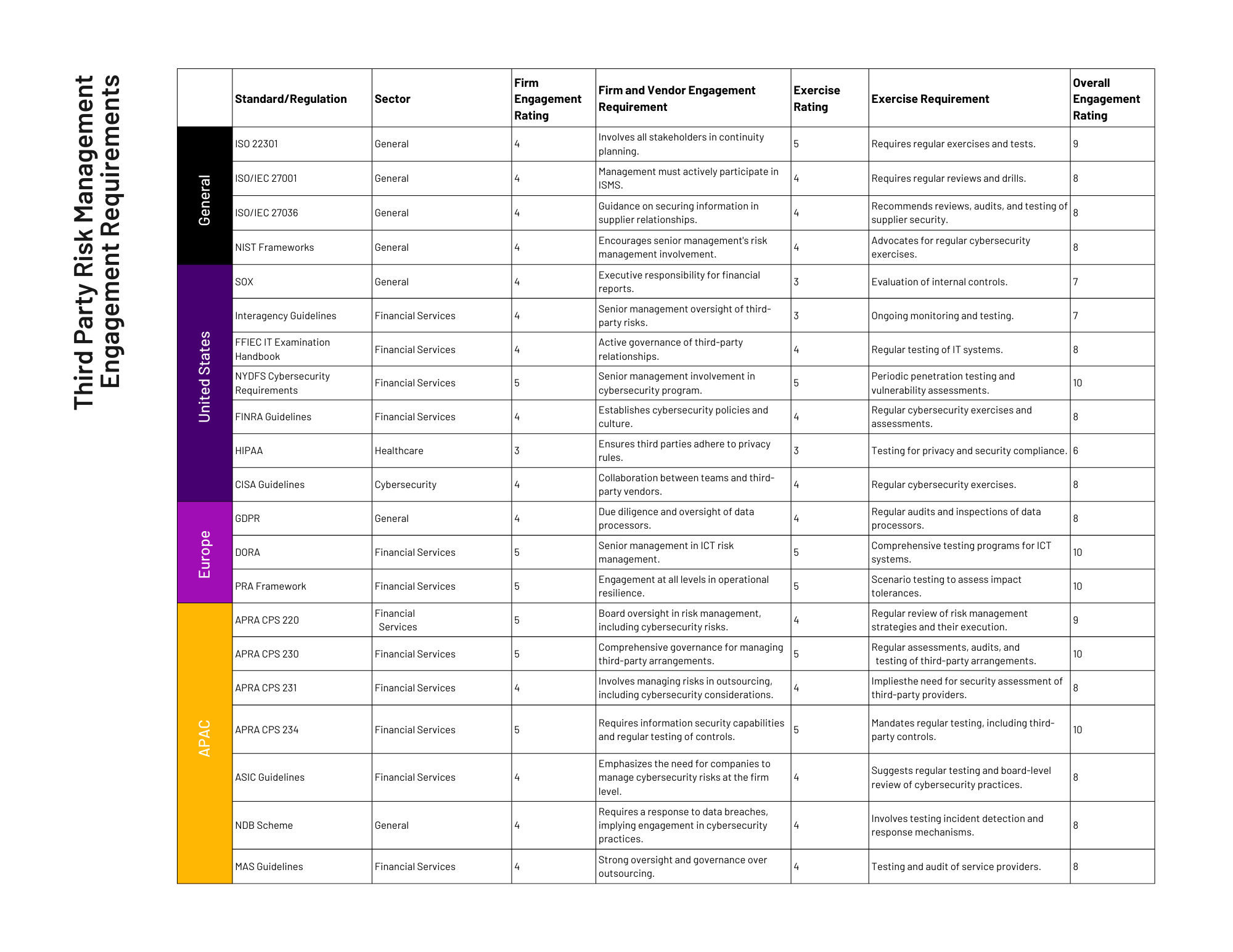
The ratings provided in the table for firm engagement and exercising/testing were assessed based on a qualitative understanding of each standard and regulation’s requirements.
Firm Engagement Rating: This rating reflects the degree to which each standard or regulation requires active involvement and commitment from senior management and other stakeholders within an organization. A higher rating indicates a greater emphasis on leadership roles, corporate governance, policy development, and the establishment of a security-conscious culture. These ratings were determined by examining how prescriptive each standard is regarding the roles and responsibilities of senior management in establishing, maintaining, and overseeing a third-party risk management program.
Exercise Rating: This rating assesses the extent to which standards and regulations mandate the performance of exercises, tests, and audits to evaluate the effectiveness of third-party risk management practices. A higher rating suggests a more stringent and frequent requirement for testing, such as regular penetration testing, scenario-based exercises, and comprehensive audits to validate the security and resilience of third-party engagements. The ratings were assigned based on the specificity and frequency of exercises and tests prescribed by each framework.
The ratings are subjective and meant to provide a relative comparison of each standard’s focus on these two aspects. They are not based on a numeric formula but on an interpretation of the standards’ documentation, expert knowledge, and industry best practices related to third-party risk management, operational resilience, and cybersecurity.
Image: ChatGPT-generated word cloud of terms most frequently used in Third Party Risk Regulations.
Shared Themes for Third-Party Risk Management
Across these standards and regulations, there are common themes in the requirements for exercising and firm engagement:
- Regular Testing and Exercises: Organizations are expected to conduct regular tests and exercises to assess and improve their operational resilience, including the resilience of third-party providers.
- Involvement of Senior Management: There is a clear expectation for senior management and, where applicable, the board of directors, to be actively involved in overseeing and managing operational resilience, including engagement with third-party risk.
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Effective operational resilience requires collaboration across various stakeholders within the organization as well as with third-party vendors, ensuring that all parties understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining resilience.
Implementing these requirements helps organizations not only comply with regulatory expectations but also strengthens their ability to respond to and recover from disruptions, protecting their critical operations and services.
Integrating the strategic focus of Microsimulations with the more more detailed and exhaustive approach of interactive tabletop exercises, engagement can bring your data to life, identifying gaps, addressing vulnerabilities, and building improved firm-level and third-party response capability.
Case Studies in Third-Party Risk Management
How are firms leveraging tools like Microsimulations and interactive tabletops to meet the evolving standard of compliance? Whether your efforts are focused on your most critical supplier or are more comprehensive, these approaches can be easily right-sized to fit the needs of your specific organization. Here are a few examples:
Financial Services: ISO 22301 (Business Continuity Management)
Problem: A multinational financial services organization identified disruptions in its international payment processing system due to geopolitical tensions, posing a risk to business continuity.
Solution: The bank utilized microsimulations to model the impact of geopolitical disruptions on payment processing. The simulations explored various scenarios, including sanctions, cyber-attacks, and communication outages, focusing on identifying critical vulnerabilities and fortifying the bank’s adaptability and response strategies.
Results: The simulations led to the development of more resilient payment processing strategies, including diversifying third-party service providers and enhancing cybersecurity measures, significantly reducing potential downtime and financial impact.
Insurance: Interagency Guidelines on Third-Party Relationships
Problem: An insurance company relied heavily on a third-party data analytics firm for processing claims data, raising concerns about data security and compliance with privacy regulations.
Solution: Through strategic microsimulations, the company assessed the potential impact of a data breach at the third-party firm. These simulations helped identify weaknesses in data handling and protection practices, focusing on scenarios that could lead to data exposure or loss.
Results: Insights from the simulations prompted the insurance company to implement stricter data security requirements and more rigorous monitoring of the third-party provider’s compliance with privacy regulations, enhancing the protection of sensitive customer data.
Technology and Telecommunications: Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) Guidelines
Problem: A leading telecommunications company faced the risk of widespread service disruption due to a sophisticated cyber-attack on its network infrastructure, potentially exploited through vulnerabilities in third-party software.
Solution: The company conducted high-level cyber threat microsimulations to identify and evaluate strategic vulnerabilities, particularly focusing on third-party software components. The simulations modeled various attack vectors, assessing the potential impact on network operations and customer service.
Results: The microsimulations revealed critical security gaps and led to the strengthening of cybersecurity defenses, including the adoption of more secure software development practices and the implementation of advanced threat detection and response mechanisms, significantly reducing the risk of future attacks.
Engagement: The Missing Piece
Mastering the intricate dance of third-party risk management and cutting through organizational chaos requires not just insight but innovation.
Imagine turning the complexities of your operations into engaging, game-like experiences that not only simplify processes but also boost capability across your team and critical third parties.
Sign up for our newsletter to learn more about how iluminr can help you harness the power of engagement and gamification to transform challenges into achievements.
Author
Paula Fontana
VP, Global Marketing
iluminr